Common cold
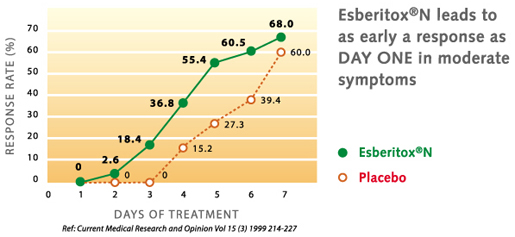
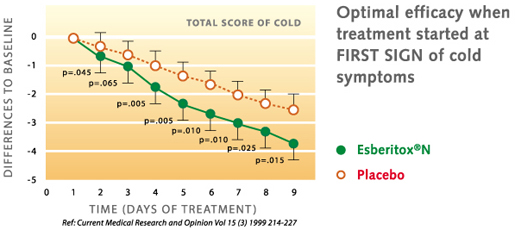
In the year 1999 a study was able to show in patients with a viral respiratory tract infection (ie common cold) that by therapy with Esberitox®N, the complaints were alleviated much faster than under placebo. The duration of the illness was shortened by two days.
Source:
H.H. Henneicke-von Zepelin et al.: Efficacy and Safety of a Fixed Combination Phytomedicine in the Treatment of the Common Cold (Acute Viral Respiratory Tract Infection): Results of a Randomised, Double Blind, Placebo Controlled, Multicentre study. Curr Medical Research and Opinion Vol.15 (3), 214-227 (1999)

Use with antibiotic
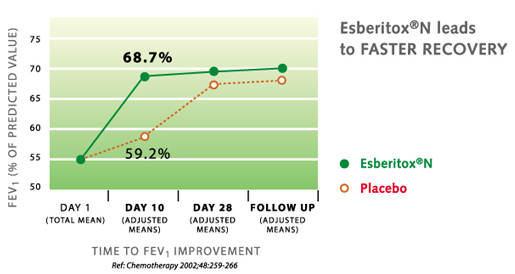
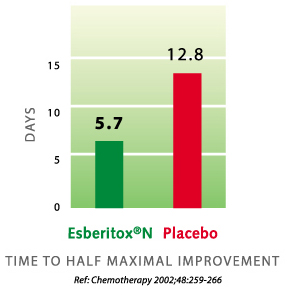
In the year 2002 a study was done on patients requiring antibiotic because of severe bacterial infection (acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis). The study shows that recovery is much faster for patients taking Esberitox®N with antibiotic rather than antibiotic by itself. Recovery is seven days faster.
Source:
Gert Kohler et al.: Esberitox®N as Supportive Therapy when Providing Standard Antibiotic Treatment in Subjects with a Severe Bacterial Infection (Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis). Chemotherapy 48,259-266 (2002)
-------------------------------
|
|
|
| |
| Clinical trials efficacy |
|
|
Faster recovery from cold |
|
|
Concomitant treatment with antibiotic |
|
|
Use of Esberitox®N in children |
|
|
|
| |
| CLINICAL STUDIES |
|
|
Clinical trials conducted with Esberitox®N |
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
Acute and Chronic Respiratory tract infections (of viral or bacterial origin)
|
| |
| Wüstenberg P, Henneicke-von Zepelin HH, Köhler G, Stammwitz U. |
Adv Ther 1999;16:
51–70. |
Efficacy and mode of action of an immunomodulator herbal preparation
containing echinacea, wild indigo and white cedar. |
|
Henneicke-von Zepelin HH, Hentschel C, Schnitker J, Kohnen R,
Köhler G, Wüstenberg P. |
Curr Med Res Opin 1999;15:214–27. |
Efficacy and safety of a fixed combination phytomedicine in the treatment of the common cold (acute viral respiratory
tract infection): results of a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled,
multicentre study. |

PDF 3.2MB |
Naser B, Lund B, Heinneicke-von Zepelin HH, Köhler G, Lehmacher W,
Scaglione F. |
Phytomedicine 2005; in press. |
A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled clinical dose–response trial of an extract of Baptisia/Echinacea and Thuja in the
treatment of patients with common cold. |

PDF 1.7MB |
| HD Reitz. |
Notabene medici (1990) 362-366. |
Immunomodulators with phytotherapeutic agents. |
|
| MD Vorberg |
Arztliche Praxis 36 (1984) 97-98. |
For colds, stimulate the nonspecific immune system |
|
|
| |
|
| |
Accompanying an antibiotics therapy in case of severe bacterial infection
|
| |
| von Blumröder WO. |
Z Allgemeinmed 1985;61:271–3. |
Angina lacunaris. |
|
| Hauke W, Köhler G, Henneicke-von Zepelin HH, Freudenstein J. |
Chemotherapy 2002;48:259–66. |
Esberitox®N as Supportive therapy when providing standard antibiotic
treatment in subjects with a severe bacterial infection (acute exacerbation
of chronic bronchitis). |

PDF 0.4MB |
| M.Zimmer. |
Therapiewoche (35) (1985), 36: 4024-4028 |
Specific conservative treatment of acute sinusitis in the ENT practice. |
|
| H.Stolze et al. |
Der Kassenarzt 23 (1983) 43-38 |
A treatment with antibiotics can be optimized by additional immunostimulation. (Acute Tonsilitis) |
|
|
| |
|
| |
Leukopenias after radiation or cytostatic treatment
|
| |
| R. Bendel et al. |
Onkologie 12 (3) 1989, 32-38 |
Adjuvant therapy with Esberitox®N in patients receiving chemo- and radiation therapy for advanced breast cancer. |
|
| |
|
| |
Herpes simplex labialis
|
| |
| H. Bockhorst |
Z allerg. Med. 58 (1982) 1795-1798 |
The treatment of herpes simplex in practice. |
|
| |
|
| |
Treatment in children
|
| |
| Kohler et al. |
Zeitschrift fur Phytotherapie 19 (1998), 318-322 |
Children’s dosage of phytopharmaceuticals: Representative, Exemplary, Age stratified Dosage practice for Esberitox®N the Herbal combination of active substances. |
| K.D. Blunck. |
Kinderartzt 14 (1983), 8:991-992 |
Susceptibility to infection at children’s home – to increase the resistance against infections. |
|
| |
|
| |
|
![]()